l1 and l2 regularization¶
Overfitting problem¶
In the previous lesson you were introduced to polynomial regression model. Despite the fact that this classifier did much better on both train and test data than the linear regression, we see a gap between its performance on train and test data. Actually, the mse score on train data was lower than on test one, which is a sign of overfitting to train data. Overfitting is a most frequently encountered problem in the supervised learning, that means that the model has a poor generalization towards new data. Overfitting occurs when our model learns very complex function in order to exactly fit all the data in training subset. Let’s consider the following example : You want to train your model to classify if the object is shoes, but the only images you have in our training data - are the photos of sneakers. Thus, when your model sees boots, it will think that it’s not shoes which is actually incorrect. One problem that can lead to overfitting, as defined in the highlighted example, is the imbalanced dataset (when there are more samples in one class than in the other) or different distribution of data. Coming back to our problem, we experience overfitting because of the complexity of the decision boundary that was learned by our algorithm. The chart shown below describes the decision boundary of polynomial regression depending on different degree of polynomial.
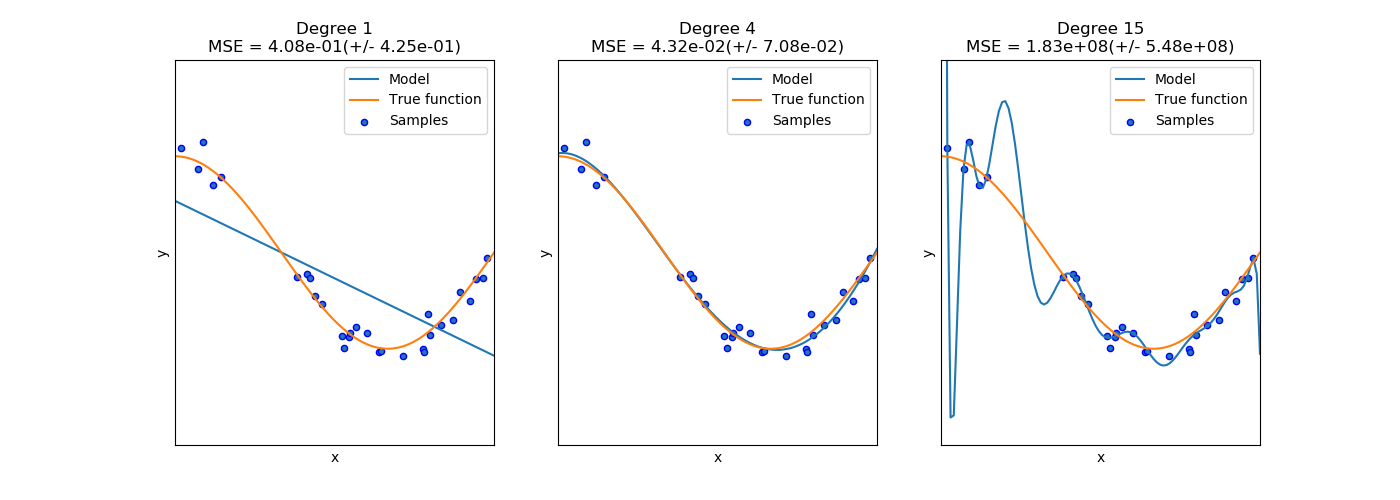
Note how the decision boundary changes with complexity of the model (with increasing the degree of polynom). Overfitting is a fundamental problem, as the only thing we are interested in - performance of the model on unseen data. Overfitting is often referred to as the problem of high variance.
Underfitting problem¶
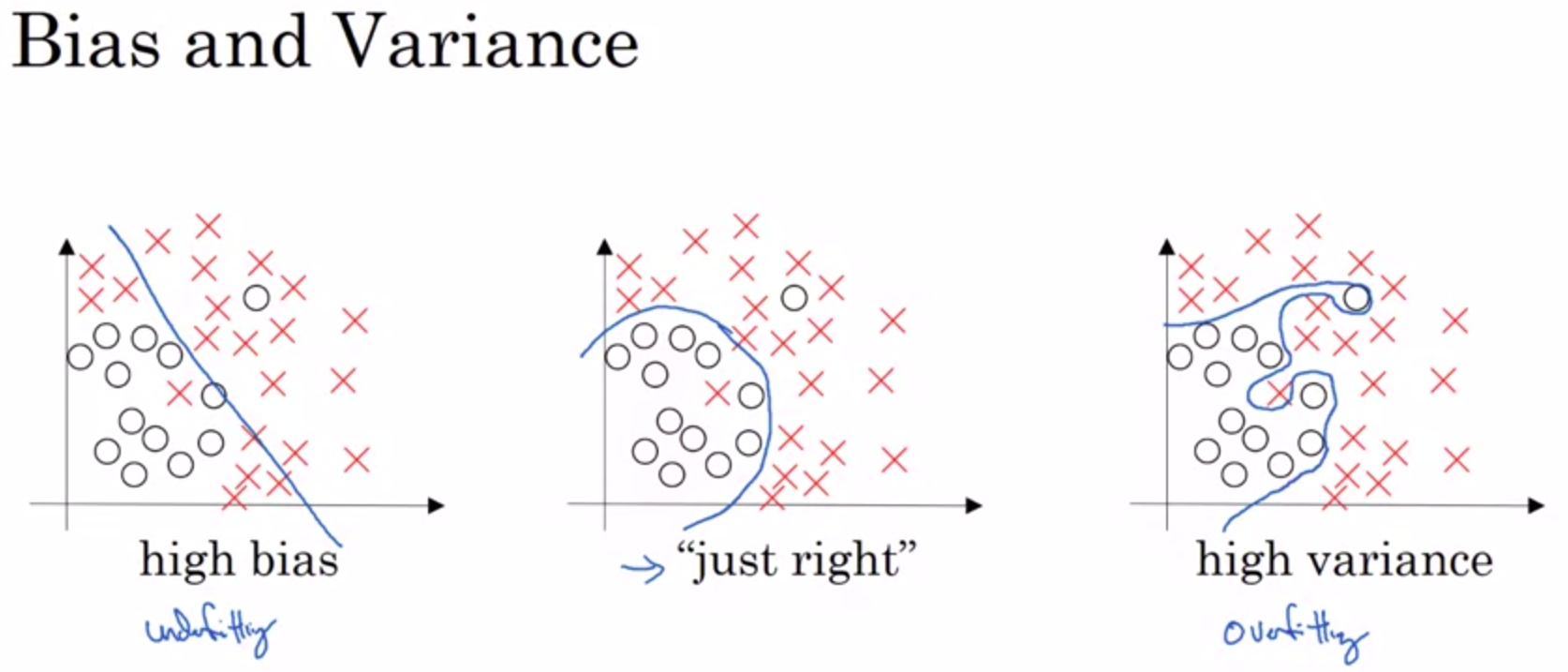
Note
We badly encourage you to take a look on this course by Andrew Ng to get more information about bias-variance trade off.
Regularization¶
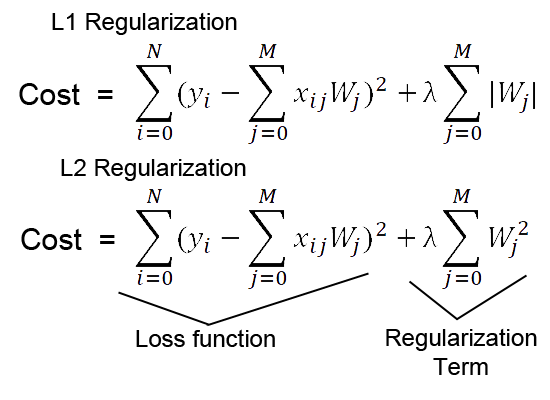
Feature normalization¶
Fit the scaler using the training set, then apply the same scaler to transform the test set.
Do not scale the training and test sets using different scalers : this could lead to random skew in data.
Do not fit the scaler using any part of the test data: referencing the test data can lead to a form of data leakage.